Let's begin with a brief, high-level explanation of middleware. In software development, middleware refers to a helper component that connects different parts of an application. It commonly acts as a mediator between a client and server, facilitating communication and data exchange.
Additionally, middleware can provide various services, including authentication, logging, caching, and more.
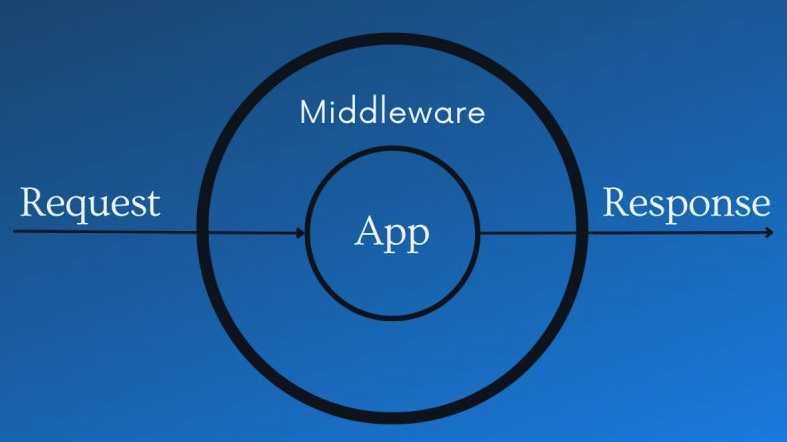
Middleware can simplify many tasks in web development, such as:
- Handling authentication and authorization
- Parsing and validating user input
- Serving static files and compressing responses
- Logging and error handling
- Adding security measures to protect against attacks
- Caching And much more.
In a specific use case, a microservice had a single endpoint for AWS health checks. The aim was to add logging and custom metrics reported to New Relic without cluttering the route method. To achieve this, middleware was utilized instead of embedding the additional functionality in the route method.
Let's take a look:
Route method (HEAD method)
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.head("/api/v1/health") # This will return 200 in case of successful request
async def health_check():
return ""
Middleware
from fastapi import Request
@app.middleware("http")
async def response_middleware(request: Request, call_next):
response = await call_next(request)
log.info(f"Healthcheck endpoint response: {response.status_code}") # Log the result
newrelic_custom_event('HealthCheckEndpoint', {'status_code': response.status_code}) # Method that will send a metric with the status code response
return response
Using middleware instead of adding all the extra logging and New Relic metric in the route method is a better approach because it helps to keep the route method clean and focused on its main purpose of handling HTTP requests and responses. By using middleware, the additional functionality such as logging and metrics can be added to the request/response pipeline in a centralized way, without cluttering the route method with extraneous code. This example might be very minimal but I hope you get the point regardless.
In addition to the above reason, this approach can also improve code maintainability and reusability since the middleware can be reused across multiple routes, rather than having to duplicate the logging and metric code in every route method.